How to Start a Chicken Farm in Georgia: A Comprehensive Guide
Time : 2025-06-30
Georgia, known for its lush landscapes and fertile soil, offers a promising environment for starting a chicken farm. Whether you’re looking to enter the poultry business for commercial purposes or as a hobby, understanding the ins and outs of setting up a successful chicken farm is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the essential steps, from planning to equipment, to help you embark on this exciting venture.
1. Market Research and Planning
Before you start your chicken farm in Georgia, it’s vital to conduct thorough market research and planning. This will help you understand the local demand for poultry products, the competition, and the potential for growth.
1.1 Identify Your Niche
Decide whether you will focus on laying hens for eggs, broilers for meat, or both. Each type of poultry requires different management techniques and market approaches.
1.2 Understand Local Regulations
Contact your local government to understand the regulations and permits required for operating a chicken farm in Georgia. These may include zoning laws, waste management, and health and safety standards.
1.3 Determine the Scale
Decide on the scale of your operation based on your initial investment, available land, and market demand. Starting small with a few hundred birds can be more manageable and less risky.
2. Site Selection and Land Preparation
The location of your chicken farm can significantly impact its success. Here are some key considerations for site selection and land preparation:
2.1 Access to Resources
Select a site with easy access to water sources, electricity, and transportation networks. These resources are essential for the daily operation of your farm.
2.2 Topography and Climate
Choose a site with a gentle slope to ensure proper drainage. Georgia’s climate is generally favorable for poultry farming, but consider the potential impact of extreme weather events.
2.3 Environmental Impact
Ensure your chosen site complies with environmental regulations and minimizes the impact on local ecosystems.
2.4 Infrastructure
Prepare the land by clearing it of debris, leveling it, and installing necessary infrastructure such as fences, waterlines, and power sources.
3. Chicken Breeds and Feed
Selecting the right chicken breeds and providing a balanced diet are critical to the success of your chicken farm.
3.1 Chicken Breeds
Choose breeds that are well-suited to Georgia’s climate and your farming goals. For example, broilers like Cornish Rocks and White Rocks are popular for meat production, while laying hens like the Red Star or Brown Leghorn are great for egg production.
3.2 Feed and Nutrition
Proper nutrition is essential for the health and productivity of your chickens. Invest in quality feed and consult with a veterinarian or poultry nutritionist to develop a balanced diet that meets the specific needs of your flock.
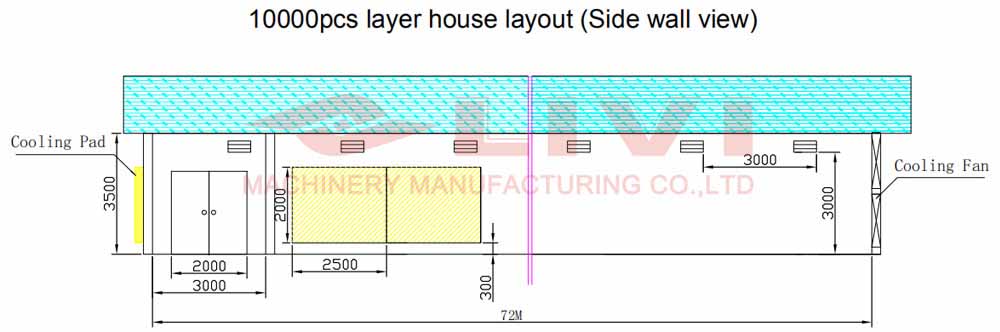
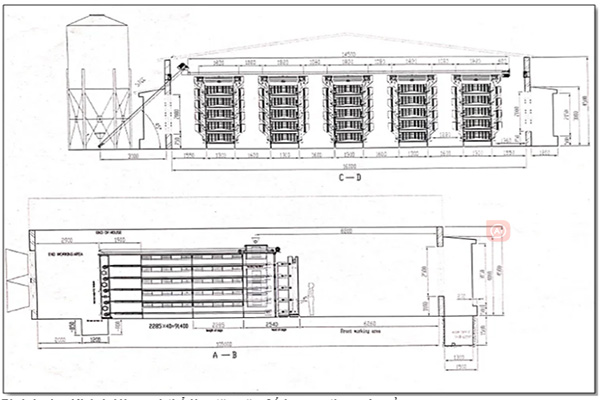
4. Equipment and Facilities
Investing in the right equipment and facilities will make your chicken farming operation more efficient and productive.
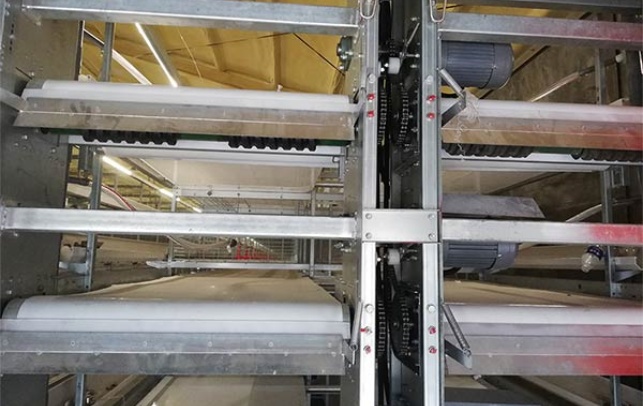
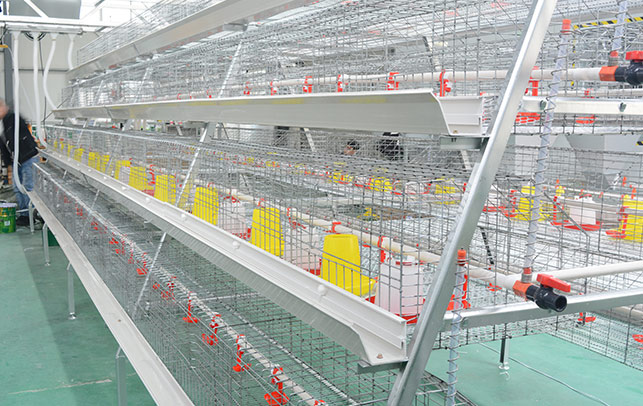
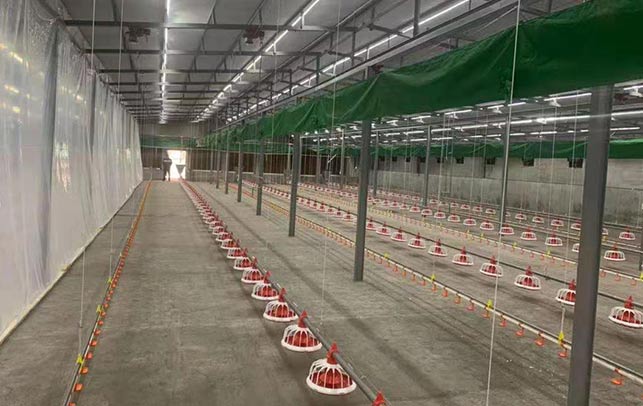
4.1 Housing
Construct sturdy, well-ventilated housing that protects your chickens from predators, extreme weather, and diseases. Consider the size of your flock and the type of poultry you’re raising when designing your chicken houses.
4.2 Feeding Equipment
Choose appropriate feeding equipment, such as automated feeders, that can accommodate your flock size and feed consumption rates.
4.3 Water Systems
Install reliable water systems with regular maintenance to ensure your chickens have access to clean, fresh water at all times.
4.4 Health Monitoring Equipment
Incorporate health monitoring equipment, such as temperature and humidity gauges, to keep track of the environment and your flock’s well-being.
5. Managing Your Chicken Farm
Proper management is crucial for the success of your chicken farm. Here are some key considerations:

5.1 Biosecurity
Implement biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction of diseases to your flock. This includes limiting access to your farm, disinfecting vehicles and equipment, and isolating new arrivals.
5.2 Monitoring and Record Keeping
Regularly monitor your chickens for signs of health issues, growth, and productivity. Keep detailed records of your flock, feed, and expenses to track your farm’s performance and make informed decisions.
5.3 Labor and Training
Hiring and training competent staff is essential for the smooth operation of your farm. Ensure your employees understand the importance of biosecurity, animal welfare, and the specific requirements of your farming operation.
6. Marketing and Sales
Develop a solid marketing plan to promote your chicken farm and its products.
6.1 Identify Your Target Market
Understand who your customers are and tailor your marketing efforts accordingly. This may include direct sales to consumers, selling to restaurants or grocery stores, or supplying to local farms.
6.2 Build Your Brand
Develop a unique brand identity for your chicken farm, highlighting the quality of your products and your commitment to sustainability and animal welfare.
6.3 Expand Your Reach
Explore various marketing channels, such as social media, farmer’s markets, and local events, to reach a wider audience.
Conclusion
Starting a chicken farm in Georgia requires careful planning, investment in quality equipment, and a commitment to good management practices. By following this comprehensive guide, you can increase your chances of success in this dynamic and rewarding industry.











