Tanzania Chicken Equipment Import: Customs Clearance Process and Best Practices
Time : 2025-06-28
The poultry industry in Tanzania is experiencing significant growth, and with it comes the need for advanced chicken equipment. Importing such equipment involves navigating a complex customs clearance process. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the customs clearance process for importing chicken equipment into Tanzania, including best practices and tips for a smooth importation.
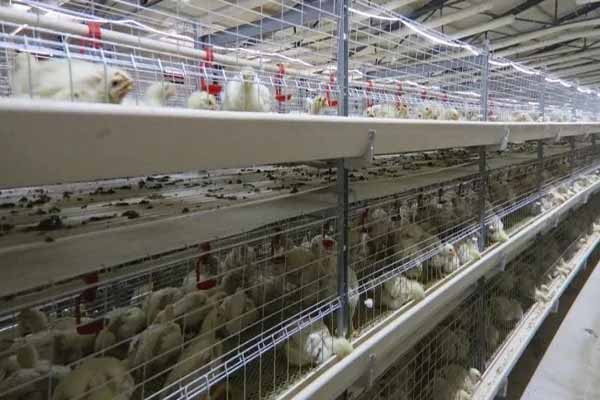

Introduction to Chicken Equipment Import in Tanzania
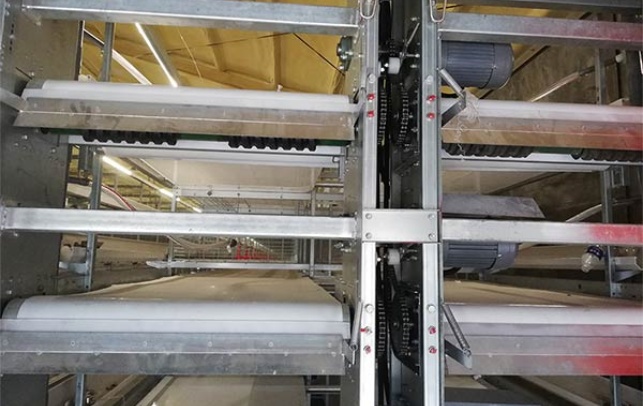
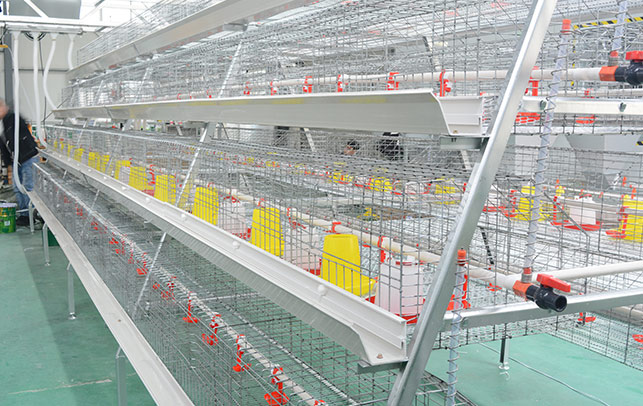
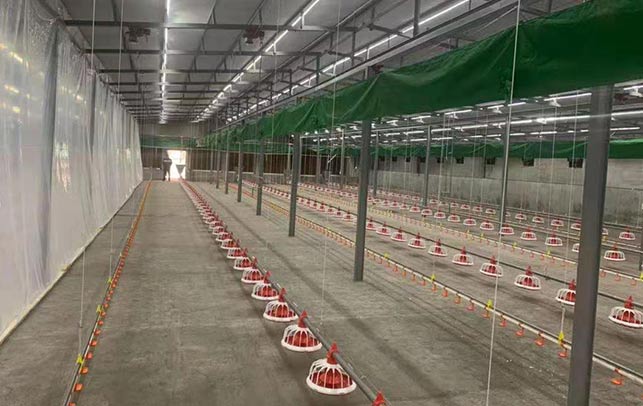
Tanzania’s poultry sector has been expanding rapidly, driven by increasing domestic demand for poultry products and the potential for export. To support this growth, the importation of high-quality chicken equipment is crucial. This includes feeders, drinkers, incubators, and other essential machinery that ensures efficient and hygienic poultry farming practices.
The Customs Clearance Process
1. Pre-Importation Requirements
Before importing chicken equipment into Tanzania, it is essential to understand the pre-importation requirements. These include:
- Import License: An import license is required for all goods entering Tanzania. This can be obtained from the Tanzania Investment Centre (TIC) or the relevant ministry.
- Bill of Lading: A bill of lading is a document that serves as evidence of the contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier. It is essential for customs clearance.
- Packing List: A detailed packing list that includes the description, quantity, and weight of each item in the shipment.
- Invoice: An invoice detailing the value of the goods, including shipping and insurance costs.
- Declaration of Conformity: A document stating that the goods comply with all applicable Tanzanian standards and regulations.
2. Classification and Valuation
Proper classification and valuation of the imported chicken equipment are critical for customs clearance. The Harmonized System (HS) code for chicken equipment typically falls under 8432.99. It is essential to use the correct HS code to avoid delays and additional charges.
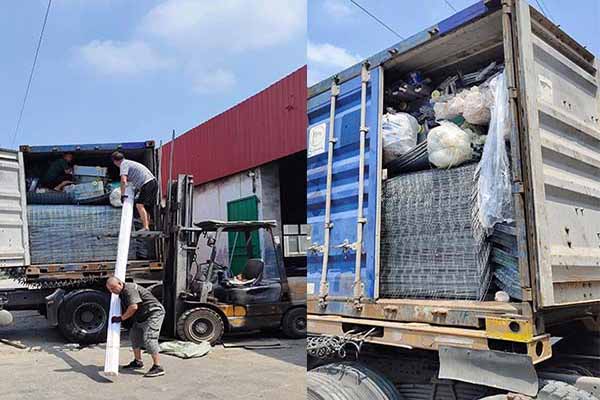

3. Customs Declaration
The importer or their authorized agent must complete a customs declaration. This declaration should include the correct HS code, description of goods, quantity, and value. It is crucial to ensure that all information is accurate to avoid complications during customs clearance.
Best Practices for Customs Clearance
1. Engage a Professional Freight Forwarder
Working with a professional freight forwarder can greatly simplify the customs clearance process. They have the expertise to handle all aspects of importation, including documentation, customs clearance, and logistics.
2. Ensure Compliance with Tanzanian Standards
It is essential to ensure that the imported chicken equipment complies with all Tanzanian standards and regulations. This includes obtaining a Declaration of Conformity and ensuring that the equipment meets local safety and hygiene requirements.
3. Proper Documentation
Accurate and complete documentation is key to a smooth customs clearance process. Double-check all documents before submission to avoid errors and delays.
4. Be Prepared for Inspection
The customs authority may request an inspection of the imported goods. Be prepared for this possibility by ensuring that the goods are properly packed and labeled. It is also advisable to have a representative available to answer any questions during the inspection.
5. Understand Duty and Tax Rates
Be aware of the duty and tax rates applicable to chicken equipment imports in Tanzania. This will help you budget for the importation costs and avoid unexpected expenses.
Conclusion
Importing chicken equipment into Tanzania requires careful planning and adherence to the customs clearance process. By understanding the requirements, engaging a professional freight forwarder, and ensuring compliance with local standards, you can navigate the process efficiently and successfully. With the right approach, you can contribute to the growth of Tanzania’s poultry industry while minimizing the risks and costs associated with importing.